Abstract
C-type asteroids1 are considered to be primitive small Solar System bodies enriched in water and organics, providing clues to the origin and evolution of the Solar System and the building blocks of life. C-type asteroid 162173 Ryugu has been characterized by remote sensing2,3,4,5,6,7 and on-asteroid measurements8,9 with Hayabusa2 (ref. 10). However, the ground truth provided by laboratory analysis of returned samples is invaluable to determine the fine properties of asteroids and other planetary bodies. We report preliminary results of analyses on returned samples from Ryugu of the particle size distribution, density and porosity, spectral properties and textural properties, and the results of a search for Ca–Al-rich inclusions (CAIs) and chondrules. The bulk sample mainly consists of rugged and smooth particles of millimetre to submillimetre size, confirming that the physical and chemical properties were not altered during the return from the asteroid. The power index of its size distribution is shallower than that of the surface boulder observed on Ryugu11, indicating differences in the returned Ryugu samples. The average of the estimated bulk densities of Ryugu sample particles is 1,282 ± 231 kg m−3, which is lower than that of meteorites12, suggesting a high microporosity down to the millimetre scale, extending centimetre-scale estimates from thermal measurements5,9. The extremely dark optical to near-infrared reflectance and spectral profile with weak absorptions at 2.7 and 3.4 μm imply a carbonaceous composition with indigenous aqueous alteration, matching the global average of Ryugu3,4 and confirming that the sample is representative of the asteroid. Together with the absence of submillimetre CAIs and chondrules, these features indicate that Ryugu is most similar to CI chondrites but has lower albedo, higher porosity and more fragile characteristics.
Main
On 6 December 2020, samples from the C-type asteroid 162173 Ryugu were returned to Earth by Hayabusa2 in a hermetically sealed container within the re-entry capsule (Tachibana, S. et al., manuscript in preparation), and transported from South Australia to the Extraterrestrial Sample Curation Center (ESCuC) in Sagamihara, Japan. Samples were recovered in a non-destructive manner and under a strict contamination-controlled conditions to perform initial descriptions before delivery for in-depth investigations by the nominated analytical teams and for future research worldwide, as detailed in the Methods and Extended Data Fig. 1. The asteroid Ryugu is the fourth extraterrestrial body of which samples have been returned to the Earth by spacecraft, following past sample return missions by Apollo13, Luna14 and Chang’e-515 from the Moon, Stardust from comet 81 P/Wild216 and Hayabusa from near-Earth S-type asteroid Itokawa17,18. The Ryugu sample has sizes ranging from ~8 mm, the largest average diameter, down to fine submillimetre dusts, with millimetre-scale particles being the most common (Extended Data Fig. 2).
A total of 5.424 ± 0.217 g was collected from Ryugu (Extended Data Fig. 2), and has been kept as physically and chemically pristine as possible, handled only in a vacuum or in purified nitrogen without exposure to Earth’s atmosphere. From Chamber A, 3.237 ± 0.002 g of samples was recovered, collected during the first touch-down sampling (TD1) at the equatorial ridge region of Ryugu10. We assume that these samples represent the surface materials of Ryugu at the uppermost centimetre-scale layer, and that this layer is influenced by insolation, radiation, temperature cycling and micrometeoritic impacts. From Chamber C, 2.025 ± 0.003 g of samples was recovered, collected during the second touch-down sampling (TD2) at a site10 proximal to the artificial crater excavated by the Small Carry-on Impactor (SCI)6,19. We assume that some of the samples in Chamber C represent subsurface materials excavated by the impact experiments, and that these samples have not experienced long-term exposure to space.
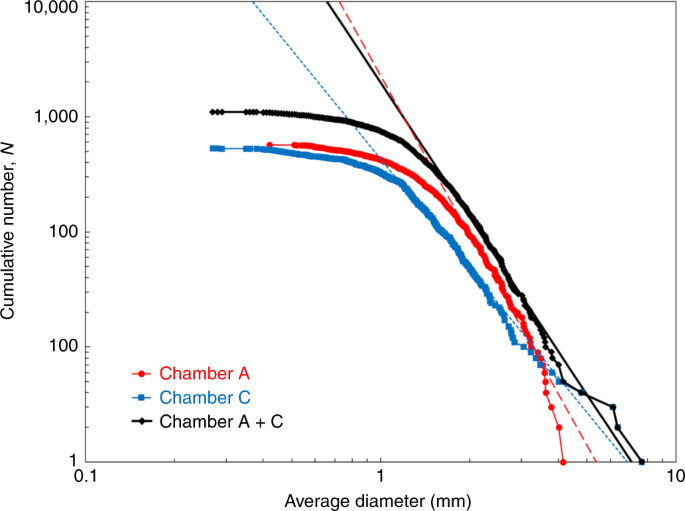
The size–frequency distributions for particles larger than 1 mm hand-picked from the bulk samples of chambers A and C were reconstructed from individual particle measurements (Fig. 1). The sample size distribution has a slope of −3.88 ± 0.25 in the power-index. This power index of Chamber A + C particles is steeper than the global average index (−2.65 ± 0.05) obtained for boulders (5–140 m in size) on Ryugu or the power-index (approximately −2) for gravels (0.02 m to several metres in size) at the local touch-down sites11 observed by the telescopic Optical Navigation Camera (ONC-T)20. The steeper power-index in the returned particles implies a higher relative abundance of the smaller particles but there are several possible interpretations for the steep power-index arise, including: the fragile nature of samples from Ryugu that may have undergone further fragmentations during impact sampling using a bullet and the cone-shaped collector21, the shock and vibration experienced during Earth entry in the sample container mounted inside the re-entry capsule22, possible artificial fractionation effects from the better transference of smaller particles through the sampler horn21 and/or a sampling bias caused by hand-picking of particles with vacuum tweezers by several personnel (as mentioned in the Methods). The power-index of Chamber A particles, −4.59 ± 0.44, is steeper than those of Chamber C, −3.15 ± 0.20, which shows a much shallower power-index in the size range larger than 3 mm. This larger size enrichment in Chamber C could indicate that such larger particles might have been excavated from regolith below Ryugu’s surface by the SCI close to site TD210,19.
A dashed red and blue line is a fitting line to the size distribution of Ryugu particles in the chamber A and C, respectively, and a solid black line is a fitting line to the size distribution of those in chambers A and C. The power-index of those in the chambers A and C (shown as Chamber A + C) is −3.88, which is much steeper than of the global average of Ryugu boulders of >5 m, −2.65 (ref. 11). This might indicate that further fragmentation occurred for smaller Ryugu grains before and/or after their recovery.
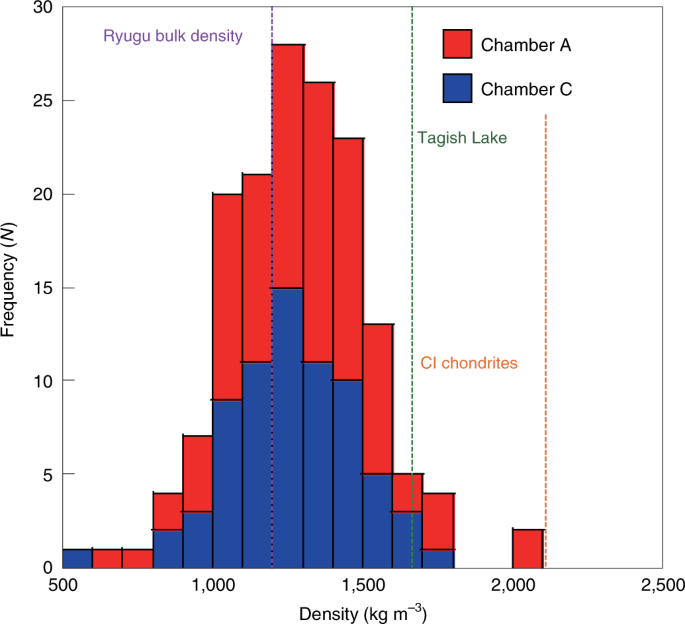
From the micrographs of Ryugu particles and their weights measured using a balance, the bulk densities of Ryugu particles could be estimated on the basis of assumptions mentioned in the Methods. The average bulk density of Ryugu particles in both chambers A and C is 1,282 ± 231 kg m−3 (Fig. 2). This is lower than the average bulk density of CI chondrites23 of 2,110 kg m−3, that of the Tagish Lake meteorite24 (1,660 ± 80 kg m−3, the most porous meteorites ever found on Earth). Assuming that millimetre-sized sample grains have the same grain density as CI chondrites (Orgueil; 2,380 ± 80 kg m−3)23, we estimate the microporosity of Ryugu samples to be 46%. Our value is consistent with the porosity determined by remote thermal imaging by the Thermal Infrared Imager (TIR)25 and on-site thermal measurements9 with the radiometer (MARA) on the Mobile Asteroid Surface Scout (MASCOT)26; this value is lower than that of meteorites, suggesting that thermal measurements made remotely at the centimetre scale can be confirmed by laboratory sample measurements made at the millimetre scale. Thus the microscopic observations and weight measurements for the Ryugu samples imply low density and/or high microporosity. The calculated bulk density of the Ryugu samples is comparable to that of Ryugu rock estimated from the bulk density of Ryugu and linear mixture packing theory: 1,380 ± 70 kg m−3 within the range of variation27.
The average sample bulk density (1,282 ± 231 kg m−3) is slightly larger than that of Ryugu (1,190 kg m−3, vertical dashed purple line)2 but much smaller than those of the Tagish Lake meteorite (vertical dashed green line)24 and CI chondrites (vertical dashed orange line)23, indicating the porous nature of Ryugu samples compared with known primitive chondrites.
Such high-microporosity materials have not been discovered in any meteorites found on Earth, probably due to break-up owing to their fragile nature during entry into the Earth’s atmosphere or a higher abundance of lower-density components such as carbonaceous materials (1,300–1,400 kg m−3)28 compared with other carbonaceous chondrites (CCs). The global average density (bulk density) of Ryugu is 1,190 ± 20 kg m−3, indicating a macroporosity of 7%, which is inconsistent with the large macroporosities required for primitive asteroids when typical meteoritic density is assumed23, provided that the returned samples collected from the two sampling sites on the surface of Ryugu are representative of bulk materials on Ryugu. The low macroporosity of Ryugu is probably consistent with the packing model using the size–frequency distribution of Ryugu29. No substantial difference in density distribution was found between chambers A and C, consistent with the same thermal properties inside and outside the artificial crater30. There are particles denser than 1,800 kg m−3 (>2σ) in Chamber A, which is within the density range of typical meteorites found on Earth12 and indicates that Ryugu might consist of a mixture of particles from different origins30 or varying degrees of alteration in the parent bodies5,30.
Optical and near-infrared reflectance profiles of the samples measured using optical microscopy, Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy and the infrared hyperspectral microscope (MicrOmega)31,32 show very dark features with an albedo of ~0.02 from 0.4 µm to 4 µm (Figs. 3 and 4), which is in good agreement with the global average of albedo3,4 observed by ONC-T and the Near Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3)33. The surface compositions and inclusions of each sample show some variety but most of them are considered representative of the typical surface materials of Ryugu as they have spectroscopically homogeneous and featureless characteristics without apparent high-temperature components (such as chondrules or Ca–Al-rich inclusions (CAI)), but have many bright and patchy fine inclusions (Extended Data Fig. 2). Although full photometric measurements are needed to elucidate the optical properties of the Ryugu samples, the apparent rarity of chondrules in Ryugu samples is consistent with predictions by a previous study27. The surface morphology of the samples is mainly classified into two patterns of rugged and smooth surfaces even at the millimetre to submillimetre scale, which is similar to the patterns found for centimetre- to metre-scale surfaces3,8 observed by ONC-T and the imager on MASCOT (MasCAM)34. The presence of different types of surface morphology may indicate past mixing processes of materials of different origin or different degrees of alteration5,7,30. The shape distribution of the particles, which has been studied in a separate paper (Tachibana, S. et al., manuscript in preparation), shows variations in aspect ratios, including elongated and flattened particles that are consistent with the ejecta observed during the sampling operations (Tachibana, S. et al., manuscript in preparation).
a, Spectra are normalized to each of continua between 2.0 µm to 4.0 µm. Both spectra show features at 2.72 µm (a vertical dashed black line in the left), corresponding to hydroxyl (OH) absorption, and 3.4 µm (a vertical dashed black line in the right), corresponding to organic molecule or carbonate adsorption. A faint absorption at 3.1 µm (a vertical dashed black line in the centre) is also confirmed in spectra of bulk samples analysed by MicrOmega, indicating the presence of a nitrogen-rich phase32. b, The same raw spectra are compared with remote-sensing data for Ryugu taken by NIRS3 with its error bars 4. The absorption feature at 2.72 µm (a vertical dashed green line) observed with NIRS3 is confirmed by the Ryugu samples. The continuum of Ryugu samples is reddenned compared with that of NIRS3, which might reflect the space weathering effect being clearer in the samples than remote-sensing data.
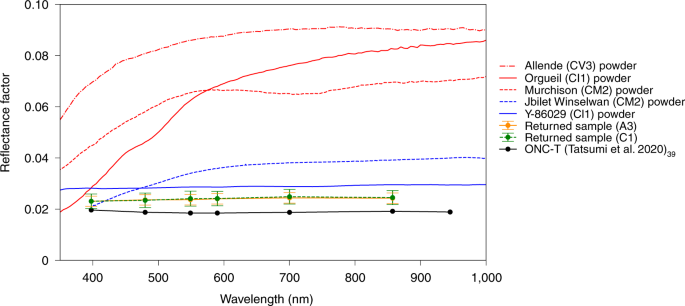
The red lines represent typical types of CC from RELAB data51 and the blue lines are unusual types of CC from RELAB and Sugita et al.3. Note that the data for each of the CCs are from powder samples within sizes ranging from <63 µm to <155 µm. Ryugu particles obtained from chambers A and C show an albedo of ~0.02 (reflectance factor at 30°, 0°, 30°), which is comparable to remote-sensing data of Ryugu’s surface taken by ONC-T3,39. Globally, Ryugu is confirmed to be much darker than most meteorites.
To conduct reconnaissance sample analyses during this curation phase, non-destructive and non-invasive characterization of the composition was performed by near-infrared spectroscopy through the two complementary instruments. Both FTIR and MicrOmega analyses for bulk samples from chambers A and C show spectral profiles. The FTIR can obtain reflectance spectrum from of 1 to 4 µm wavelength range with a footprint of ~6 mm diameter (Fig. 3), and the MicrOmega can analyze hyperspectral image-cubes of 256 × 256 pixels (22 µm pixel size), with up to 400 spectral channels covering the 0.99–3.65 µm spectral range. Both exhibit clear absorption features at 2.7 µm and 3.4 µm, for both samples. The narrow and relatively deep (~15%) absorption feature at 2.72 µm indicates the presence of hydroxyl (OH) in the samples, which is comparable to the 2.72 µm absorption feature detected across the surface of Ryugu by NIRS34 but the position of the absorption peak is in better agreement with the materials excavated by the SCI impact experiment35. MicrOmega high spatial resolution enabled us to identify a few submillimetre grains with distinct and highly diagnostic spectral features. As an example, an absorption centred at 3.4 µm, also present in FTIR spectra, corresponds to both carbonates and CH-rich phases. Similarly, an absorption centred at 3.1 µm is interpreted as relating to NH-rich compounds as it has been postulated to be similar to that observed on 1 Ceres36. These detections are evidence of aqueous alteration of Ryugu’s parent body and consistent with the non-detection of high-temperature components like chondrules and CAIs. They point towards the Ryugu parent body being more similar to CI chondrites than to any other type of meteorite found on Earth (Table 1). Details of the MicrOmega findings are presented in a companion paper32.
High-resolution (5 µm per pixel) optical microscopic imaging through six filters, compatible with the ONC-T camera of Hayabusa23,737, was conducted on bulk samples from chambers A and C (Fig. 4). The disk-averaged spectra and reflectance of Earth-returned samples from 0.39 to 0.85 µm (ul to x bands on ONC-T) agree well with those of Ryugu3; very flat spectra consistent with Cb-type asteroids classified by ground-based observations38 and low reflectance (0.02 at the v band) under the geometric condition with incidence, emission and phase angles of 30°, 0° and 30°, respectively. This agreement indicates that Earth-returned samples represent the Ryugu surface materials well. The visible and infrared reflectance of the samples from chambers A and C are both brighter than those of remote-sensing data taken by ONC-T3,39 and NIRS34,35 beyond their observation and analytical errors (Figs. 3 and 4). This may be due to differences in surface conditions of regolith particles between the asteroid surface, on which they might be covered by fine powdery materials, and obtained samples, which might expose their surfaces when they experienced disturbances during the sampling process, and/or the possible contribution of reflected light from the bottom surface of the sapphire dishes. The infrared reflectance of the bulk samples from Chamber A is brighter than that of the samples from Chamber C in data acquired by both FTIR and MicrOmega, although some variations in wavelength exist in the MicrOmega results32. This tendency is inconsistent with results from the NIRS3 observation, which shows deeper absorption in 2.72 µm close to site TD2 site compared with other surface materials on Ryugu35. Although optical and infrared microscopic images show that Ryugu sample particles exhibit many bright spots (Extended Data Fig. 2), most bright spots disappear in different viewing geometries and so are not intrinsic to compositional variation (for example, CAIs and chondrules) but caused by different photometric conditions32. Many bright spots are found on the surfaces of boulders in the on-asteroid images8, but most may be caused by photometric effects.
Our initial observations in the laboratory for the entire set of returned samples demonstrate that Hayabusa2 retrieved a representative and unprocessed (albeit slightly fragmented) sample from Ryugu. Our data further extends an idea based on the remote-sensing observations that suggested that Ryugu is dominated by hydrous CC-like materials, similar to CI chondrites, but with a darker, more porous and more fragile nature. This inference should be further corroborated by in-depth investigations hereafter by state-of-the-art analytical methods with higher resolution and precision. The initial descriptions by Hayabusa2 provide a good signpost for future sample returns missions and their curation.
Methods
Hayabusa2 sample recovery and transportation to the ESCuC
On 5 December 2020, the re-entry capsule was released from the spacecraft and it entered the Earth’s atmosphere on 6 December 2020, after a successful return cruise from Ryugu to the Earth. The re-entry capsule retrieval operation was carried out under strict compliance with Australian COVID-19 regulations. The landing area of the capsule was determined from a beacon signal transmitted by the capsule using five antennas installed at different locations. The Marine radar systems and two drones were also used for this operation to retrieve the capsule, heat shields and parachute. The re-entry capsule was located near the parachute, which was found by helicopter observation. A safety check of the capsule was first completed at the landing location because pyrotechnic devices were used for parachute deployment and separation. No damage to the capsule was observed, and the capsule was transported back to a quick look facility prepared in the Woomera Prohibited Area with permission from the Australian safety officer. The re-entry capsule was recovered from the landing site in the Woomera Prohibited Area, South Australia, 5 h after landing, and transported to the quick look facility. The capsule was placed in a clean booth in the quick look facility; the sample container was then extracted from the capsule and its outer surface cleaned after a safety check (see also Extended Data Fig. 1). The temperature monitor attached to the sample container indicated that the container was never heated up to 65 °C, which is much lower than the outgassing temperature of water, ~100 °C.
The container was installed on the Hayabusa2 GAs Extraction and Analysis system. After overnight evacuation of the vacuum line of the GAs Extraction and Analysis system, on 7 December the bottom of the sample was pierced with a tungsten carbide needle to release volatile components of the sample held inside the container22. The container was in a vacuum, indicating that the container seal held during re-entry and no terrestrial contamination took place. The gas extracted from the sample container was split into four gas tanks at room temperature, and the residual gas in the system was then trapped in two gas tanks cooled at the temperature of liquid nitrogen. A fraction of the gas was analysed by a quadrupole mass spectrometer (WATMASS, Tokyo Electronics). The sample container was put into a nitrogen-purged antivibration transportation box and was safely transported to the ESCuC in the Sagamihara Campus of JAXA on 8 December 2020 (~57 h after the capsule landed). A heat shield made of carbon-reinforced plastic was then removed from the outer lid of the container after drilling work with a milling machine to expose the heads of the bolts and remove them. The Hayabusa2 sample container was sealed with a metal-to-metal sealing system21,22. The container lid was pressed against the container edge with a pressure load of ~2,700 N by pressure springs. To open the container in the clean chamber designed for Ryugu samples in a vacuum, the container was installed into the container opening system. The pressure springs and the outer lid with latches were then removed from the container while the pressure load was kept constant. The container with the opening system was then attached to the clean chamber, which was designed to keep the Ryugu samples in a vacuum, on 11 December (132 h after it landed) and was opened on 14 December 2020 after the chamber was evacuated.
As the outer surface of the container had been cleaned, the outer lid was first anchored to access the inner lid, then the inner lid was anchored with rods to remove the outer lid and the frame for the latches. Finally, the inner lid was anchored by the container opening system (Extended Data Fig. 1).
The clean room and clean chambers for Hayabusa2
The concept of Hayabusa2 curation was to initially make non-destructive measurements and to deliver samples for further detailed investigations without any contamination from terrestrial materials or exposure to the terrestrial atmosphere. The ESCuC was therefore equipped to the ISO 6 or Class 1000 clean room protocol (1,000 dust particles of ≥0.5 µm in diameter in cubic feet)40. The clean chambers for Hayabusa2-returned samples were prepared to handle samples under a vacuum or ultra-purified nitrogen atmosphere without exposure to the terrestrial atmosphere41. They comprise five independent chambers: CC3-1 for opening the container in a vacuum, CC3-2 for opening Chamber A of the catcher and removing a few particles in a vacuum, CC3-3 for exchanging the environment from a vacuum to purified nitrogen, CC4-1 for dismantling the catcher to extract the samples from each chamber, and CC4-2 for observation and weighing of the samples. All of the sample containers, pick-up devices, handling tools and other jigs and tools used in the clean chambers were specially cleaned to avoid contamination and were made from materials that were highly controlled to minimize the possibility of chemical reactions with the samples42.
Retrieval of Hayabusa2 samples from the container
As the sample container opening system was connected to CC3-1 with dry air overflowing from the chamber, the chamber was evacuated to reach a high vacuum (10−6 Pa). The chamber was then in a static vacuum condition for the inner lid of the container to be opened. Soon after the container was opened, the chamber was evacuated again. The sample catcher (which is combined with the inner lid) was extracted from the container and the bottom of the container was left behind. The catcher was then turned upside down so the cover of Chamber A of the catcher faced upwards and it was transported from CC3-1 to CC3-2; a gate valve between them was then closed. In CC3-2 in vacuum conditions, the surface of the cover of the Chamber A was cleaned with a Teflon spatula. All of the screw bolts of the cover were then unscrewed and the cover was removed with an electrostatic chuck to expose the samples inside Chamber A of the catcher. A large numbers of black particles of millimetre size or larger were observed inside Chamber A.
A few particles of millimetre size were removed from the chamber with a sample handling tool equipped inside the CC3-2 and put into a quartz glass dish. A cover made of quartz glass was attached to the opening of Chamber A of the catcher; the catcher was then transported from CC3-2 to CC3-3 and the gate valve between them was closed. CC3-1 and CC3-2 continued to evacuate after that. CC3-3 was slowly purged with purified nitrogen to reach atmospheric pressure. After that, the catcher was handled with tools and jigs manipulated with Viton-coated butyl gloves equipped in the CC3-3, CC4-1 and CC4-2. First, a jig for handling was attached to the catcher and the screw bolts that connected the catcher with the inner lid were removed to separate the catcher from the lid.
The catcher was next transported to CC4-2 through CC4-1 to measure its weight with a balance equipped in the CC4-2. Given the design weight of the catcher and a tare weight of the attached jig, the total weight of samples inside the catcher was calculated to be 5.424 ± 0.217 g. The balance was a Mettler-Toledo XP404s, with an outer cover modified to one made of stainless steel 304 sealed with Viton, and with the power and signal cables modified from the originals to ones coated by Teflon.
An optical microscope Nikon SMZ1270i with an XYZ electric motors system was equipped above the CC4-2, and black particles inside Chamber A of the catcher were photographed with the microscope. The catcher was then transported to CC4-1 and it was dismantled with tools and jigs to transfer samples from each of the chambers (A, B and C) to containers made of sapphire glass (see supplement for its spectral feature) set underneath funnels made of stainless steel 304. After several large particles were hand-picked directly from the opening of the funnels with a vacuum tweezer, samples from chambers A and C were divided from the funnels into three sapphire containers with a spatula made of stainless steel. Samples inside Chamber B, which was exposed to the sampler horn after site TD1 and before site TD210, were also recovered into a sapphire container and comprise only a small amount of powder (13 ± 0.5 mg). Only a limited number of samples enters into the chamber B, indicating that only a small amount of the samples should be mixed up between three chambers. The samples in the sapphire containers were weighed with a balance and spectrally characterized with FTIR, MicrOmega and visible spectrometers. Next, particles of >1 mm in size were individually hand-picked with a vacuum tweezer that had a nozzle made of stainless steel 304 and deposited into a sapphire dish; individual particles were then photographed, weighed and measured with FTIR and MicrOmega.
These obtained data are catalogued for further detailed research that started in the summer of 2021. The sample will be made available to the community and distributed through the Hayabusa2 Sample Allocation Committee in the summer of 2022.
Outline of measurements for sample description
Multiband optical images of the Ryugu samples were taken using a nadir-viewing camera system with a macro lens and a monochrome CMOS detector (Kiralux CS895MU) with illumination at 30° from the nadir43. We used six filters (ul: 0.39 µm, b: 0.48 µm, v− 0.55 µm, Na: 0.59 µm, w− 0.70 µm, x: 0.85 µm) compatible with ONC-T of Hayabusa23,20,21 to illuminate the samples for macro-lens measurements.
Spectroscopy of Ryugu samples
The FTIR used for this study was a JASCO VIR-300, equipped to CC4-2. It can measure in the infrared spectrum between 1.0 µm and 4.0 µm wavelengths. Its minimum beam spot size in the focused position is 1 mm, and a nominal beam spot for bulk sample measurement size is 6 mm. The incident beam comes through a sapphire viewport to illuminate samples inside an FTIR chamber attached to CC4-2 (with a purified nitrogen condition). Before and after the sample measurement, the incident and emission angles of the infrared light were designed to be 16°, thus phase angle for the samples is 32°. The NIRS3 spectrum was created by averaging 128 spectra acquired on 15 May 2019 (see extended data table 2 of Kitazato et al.35 for details). Its reflectance values have been corrected to the same viewing geometry (incidence,16°; emission, 16°, phase, 32°) using the latest photometric model44. Error bars are 1σ. The instrument, which includes incident and reflected light paths, was purged with nitrogen to decrease the influences of absorption of atmospheric molecules such as H2O and CO2. Infragold was measured before sample measurement to compensate for the background. No obvious effect from the sapphire containers was detected in the bulk sample analyses.
The detailed method for MicrOmega analyses is detailed in another paper32. MicrOmega was mounted on a dedicated chamber attached to CC3-3. The samples are analysed on an XYZ and θ moving stage under the nitrogen-purged conditions, and observed with MicrOmega through the sapphire window.
Size distribution and density determination of Ryugu particles
The sizes of Ryugu particles were measured from optical microscope images taken after their separation into individual containers. Note that particles were separated using tweezers by various curatorial members of the ESCuC, which may have caused a sampling bias. For the analyses of their size distributions, the major and minor diameters were calculated on the basis of eclipses circumscribed from the binarized images of particles, and averages of the major and minor diameters were used as the sizes of the particles. A cumulative number of particles versus their average diameters are plotted as Fig. 1, and a power-index fitting to the distribution was calculated by maximum-likelihood fitting methods with goodness-of-fit tests based on the Kolmogorov–Smirnov statistic45,46.
The volume of a given hand-picked particle, its size, Dp, was calculated as follows:
where a and b are the major and minor Fetet diameters, respectively, measured from its optical microscopic image and t is thickness, measured by focusing on the top and bottom of the particle using the optical microscope. Using Dp calculated from equation (1), the volume of a Ryugu particle was calculated using the following formula based on ref. 47:
The densities of the particles were calculated from the volumes obtained with the formula and weights measured with the balance in CC4-2 (Fig. 2). Typical errors in the density calculations range from 30 to 500 kg m−3, mainly due to uncertainties in the estimation of their volumes. The estimated volumes should include all of the pores inside sample particles; thus the calculated densities correspond to bulk densities of the particles, not grain densities, which are calculated on the basis of volumes excluding pores inside the particles.
Data availability
Here we note that all source data for the figures in this article is provided in the Supplement Items. Source data are provided with this paper.
References
Rivkin, A. S. et al. in Asteroids IV (eds Michel, P. et al.) 65–87 (Univ. Arizona Press, 2015).
-
Watanabe, S. et al. Hayabusa2 arrives at the carbonaceous asteroid 162173 Ryugu—a spinning top-shaped rubble pile. Science 364, 268–272 (2019).
-
Sugita, S. et al. The geomorphology, color, and thermal properties of Ryugu: implications for parent-body processes. Science 364, eaaw0422 (2019).
-
Kitazato, K. et al. Surface composition of asteroid 162173 Ryugu as observed by the Hayabusa2 NIRS3 instrument. Science 364, 272–275 (2019).
-
Okada, T. et al. Highly porous nature of a primitive asteroid revealed by thermal imaging. Nature 579, 518–522 (2020).
-
Arakawa, M. et al. An artificial impact on the asteroid162173 Ryugu formed a crater in the gravity-dominated regime. Science 368, 67–71 (2020).
-
Morota, T. et al. Sample collection from asteroid (162173) Ryugu by Hayabusa2: implications for surface evolution. Science 368, 654–659 (2020).
-
Jaumann, R. et al. In-situ investigation of asteroid (162173) Ryugu by the Mobile Asteroid Surface Scout (MASCOT) camera (MASCam). Science 465, 817–820 (2019).
-
Grott, M. et al. Low thermal conductivity boulder with high porosity identified on C-type asteroid (162173) Ryugu. Nat. Astron. 3, 971–976 (2019).
-
Tsuda, Y. et al. Hayabusa2 mission status: landing, roving, and cratering on asteroid Ryugu. Acta Astron. 171, 42–54 (2020).
-
Michikami, T. et al. Boulder size and shape distributions on asteroid Ryugu. Icarus 331, 179–191 (2019).
-
Flynn, G. J. et al. Physical properties of the stone meteorites: implications for the properties of their parent bodies. Chem. Erde 78, 269–298 (2018).
-
Turner, G. Argon-40/Argon-39 dating of Lunar rock samples. Science 167, 466–468 (1970).
Barsukov, V. L. Preliminary data for the regolith core brought to earth by the automatic lunar station Luna 24. In Proc. 8th Lunar Science Conference 3303–3318 (Lunar and Planetary Institute, 1977).
-
Qiao, L. et al. China’s Chang’e-5 landing site: geology, stratigraphy, and provenance of materials. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 561, 116855 (2021).
-
Brownlee, D. et al. Comet 81P/Wild 2 under a microscope. Science 314, 1711–1716 (2006).
-
Nakamura, T. et al. Itokawa dust particles: a direct link between S-type asteroids and ordinary chondrites. Science 333, 1113–1116 (2011).
-
Nakamura, E. et al. Space environment of an asteroid preserved on micrograins returned by the Hayabusa Spacecraft. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 109, E624–E629 (2012).
-
Saiki, T. et al. The Small Carry-on Impactor (SCI) and the Hayabusa2 impact experiment. Space Sci. Rev. 208, 165–186 (2017).
-
Kameda, S. et al. Preflight calibration test results for Optical Navigation Camera Telescope (ONC-T) onboard the Hayabusa2 spacecraft. Space Sci. Rev. 208, 17–31 (2017).
-
Sawada, H. et al. Hayabusa2 sampler: collection of asteroidal surface material. Space Sci. Rev. 208, 81–106 (2017).
-
Okazaki, R. et al. Hayabusa2 sample catcher and container: metal-seal system for vacuum encapsulation of returned samples with volatiles and organic compounds recovered from C-type asteroid Ryugu. Space Sci. Rev. 208, 107–124 (2017).
-
Britt, D. T. & Consolmagno, G. J. Stony meteorite porosities and densities: a review of the data through 2001. Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 38, 1161–1180 (2003).
-
Zolensky, M. E. et al. Mineralogy of Tagish Lake: an ungrouped type 2 carbonaceous chondrite. Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 37, 737–761 (2002).
-
Okada, T. et al. Thermal infrared imaging experiments of C-type asteroid 162173 Ryugu on Hayabusa2. Space Sci. Rev. 208, 255–286 (2017).
-
Grott, M. et al. The MASCOT radiometer MARA for the Hayabusa2 mission. Space Sci. Rev. 208, 413–431 (2017).
-
Herbst, W. et al. The macroporosity of rubble pile asteroid Ryugu and implications for the origin of chondrules. Planet. Sci. J. 2, 110 (2021).
-
Néri, A. et al. A carbonaceous chondrite and cometary origin for icy moons of Jupiter and Saturn. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 530, 115920 (2020).
-
Grott, M. et al. Macroporosity and grain density of rubble pile asteroid (162173) Ryugu. J. Geophys. Res. 125, e2020JE006519 (2020).
Sakatani, N. et al. Anomalously porous boulders on (162173) Ryugu as primordial materials from its parent body. Nat. Astron. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41550-021-01371-7 (2021).
-
Bibring, J.-P. et al. The MicrOmega Investigation onboard Hayabusa2. Space Sci. Rev. 208, 401–412 (2017).
Pilorget, C. et al. First analyses by MicrOmega of the samples returned to Earth by the Hayabusa2 mission. Nat. Astron. DOI: 10.1038/s41550-021-01549-z (this issue).
-
Iwata, T. et al. NIRS3: The Near Infrared Spectrometer on Hayabusa2. Space Sci. Rev. 208, 317–337 (2017).
-
Jaumann, R. et al. The camera of the MASCOT asteroid lander on board Hayabusa2. Space Sci. Rev. 208, 375–400 (2017).
-
Kitazato, K. et al. Thermally altered subsurface material of asteroid (162173) Ryugu. Nat. Astron. 5, 246–250 (2021).
-
Usui, F. et al. AKARI/IRC near-infrared asteroid spectroscopic survey: AcuA-spec. Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn 71, 1–41 (2019).
-
Tatsumi, E. et al. Updated inflight calibration of Hayabusa2’s Optical Navigation Camera (ONC) for scientific observations during the cruise phase. Icarus 325, 153–195 (2019).
Bus, S. J. and Binzel, R. P. Phase II of the small main-belt asteroid spectroscopic survey: a feature-based taxonomy. Icarus 158, 146–177 (2002).
-
Tatsumi, E. et al. Global photometric properties of (162173) Ryugu. Astron. Astrophys. 639, A83 (2020).
-
McCubbin, F. et al. Advanced curation of astromaterials for planetary science. Space Sci. Rev. 215, 48 (2019).
-
Yada, T. et al. Hayabusa-returned sample curation in the Planetary Material Sample Curation Facility of JAXA. Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 49, 135–153 (2014).
Yoshitake, M. et al. Cleanliness Level of the Extraterrestrial Sample Curation Center of JAXA Research and Development Report No. JAXA-RR-20-004E (JAXA, 2021).
Cho Y. et al. Development of a multispectral stereo-camera system comparable to Hayabusa2 Optical Navigation Camera (ONC-T) for observing samples returned from asteroid Ryugu. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.13480 (2021).
Pilorget, C. et al. Global-scale albedo and spectro-photometric properties of Ryugu from NIRS3/Hayabusa2, implications for the composition of Ryugu and the representativity of the returned samples. Icarus 355, 114126 (2021).
-
Clauset, A. et al. Power-law distributions in empirical data. SIAM Rev. 51, 661–703 (2009).
-
Tancredi, G. et al. Distribution of boulders and the gravity potential on asteroid Itokawa. Icarus 247, 279–290 (2015).
-
Bagheri, G. H. et al. On the characterization of size and shape of irregular particles. Powder Technol. 270, 141–153 (2015).
Hutchison, R. Meteorites: A Petrologic, Chemical and Isotopic Synthesis (Cambridge Univ. Press, 2004).
-
Nakamura, T. et al. Mineralogy and noble-gas signatures of the carbonate-rich lithology of the Tagish Lake carbonaceous chondrite: evidence for an accretionary breccia. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 207, 83–101 (2003).
-
Hezel, D. C. et al. Modal abundances of CAIs: implications for bulk chondrite element abundances and fractionations. Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 43, 1879–1894 (2008).
-
Pieters, C. M. Strength of mineral absorption features in the transmitted component of near‐infrared reflected light: first results from RELAB. J. Geophys. Res. 88, 9534–9544 (1983).
Acknowledgements
The Hayabusa2 mission has been led by JAXA, in collaboration with DLR (German Space Center) and CNES (French Space Center), and was also supported by NASA, the ASA (Australian Space Agency) and other universities and institutes. We thank all of the members of the Hayabusa2 project team for their technical and scientific contributions to the successful return of the asteroid samples to Earth. This research is partly supported by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) under KAKENHI grant numbers JP17H06459, JP18K03830, JP19K03958, JP19K23473, JP20K14548, JP19K23474, JP21K13986, JP20K14535, JP19H00725, JP19KK0094, JP20H00202, JP18K18795, JP18H04468, JP15H05695, JP16H06348 and JP19H01951, the Core-to-Core programme ‘International Network of Planetary Sciences’ and the Australian Research Council (grant number DP210101798). The activities of the Institut d’Astrophysique Spatiale are supported by the Centre National d’Etudes Spatiales, France.
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Peer review information Nature Astronomy thanks Beth Clark and Hannah Kaplan for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Extended data
A flowchart of a series of processes for the Hayabusa2 sample container and its catcher experienced after its landing. Note that samples inside the container were only exposed to vacuum and nitrogen environment in the clean chambers for Haybusa2-returned samples.
Optical microscopic images of bulk samples from Chambers A and C. (a)~(c) are those from the Chamber A and (d)~(f) are those from the Chamber C. Both samples are aggregation of black-colored mm-sized pebbles and sub-mm sized fine powder, which are not so different from each other. In total, more than five thousands particles of >100 µm2 are recognized from the images.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Fig. 1 and Materials.
Source data
Source numerical data for viewgraph of figure 1.
Source numerical data for viewgraph of figure 2.
Source numerical data for viewgraph of figure 3a.
Source numerical data for viewgraph of figure 3b.
Source numerical data for viewgraph of figure 4.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Yada, T., Abe, M., Okada, T. et al. Preliminary analysis of the Hayabusa2 samples returned from C-type asteroid Ryugu. Nat Astron (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41550-021-01550-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Further reading
-
- Beth Ellen Clark
Nature Astronomy (2021)
-
- C. Pilorget
- T. Okada
- J.-P. Bibring
Nature Astronomy (2021)
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
[ comments ]